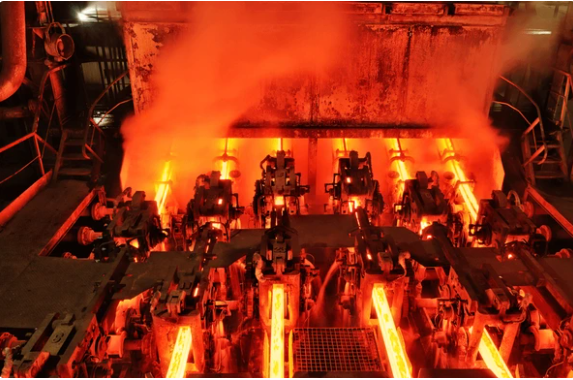
Continuous casting machines have truly transformed the metalworking industry, paving the way for the seamless production of high-quality metal shapes without any interruptions. This process is at the core of modern manufacturing, where molten metal is poured into a continuous casting machine, eventually solidifying into the desired shape and dimensions.
Let’s explore the fascinating world of continuous casting and understand why it’s such a big deal in metal production today.
Definition of Continuous Casting
Think of continuous casting as a method that keeps the metal flowing non-stop. Unlike traditional casting methods where metal is poured into moulds to create individual pieces, continuous casting allows for a continuous stream of metal to be shaped into various forms like slabs, billets, and blooms.
Explore Our Range of Deublin Rotary Unions for CCM & Other Applications
Importance in Metal Production
Continuous casting is more than just a fancy technique—it’s a game-changer in the metalworking world. By skipping intermediate steps and minimizing waste, continuous casting makes production more efficient and cost-effective. Plus, it ensures that the metal products we get are top-notch and consistent, meeting the high standards of different industries.
Historical Context
The roots of continuous casting go way back to the late 19th century, but it really took off in the mid-20th century thanks to advancements in metallurgical technology. Since then, continuous casting has evolved significantly, making production processes more efficient, improving product quality, and contributing to sustainability in the global manufacturing sector.
How Continuous Casting Works
Continuous casting relies on a series of interconnected components within a specialized machine to turn molten metal into a continuous strand of the desired shape and size. Let’s take a closer look at how this fascinating process unfolds:
Basic Principles
Continuous casting is all about controlling the cooling and solidification of molten metal to create a seamless strand. It’s like orchestrating a symphony of temperature control, mold design, and cooling techniques to ensure that the final product meets all the desired specifications.
Components of Continuous Casting Machines
Continuous casting machines consist of several key components, each playing a crucial role in the casting process. These include:
- Tundish: A reservoir that holds the molten metal and feeds it into the casting mould.
- Mold: A water-cooled container where the molten metal solidifies into the desired shape.
- Rollers: Mechanisms that support and guide the solidifying metal strand as it exits the mould.
- Cooling System: Water sprays or jets that rapidly cool the metal strand to facilitate solidification.
- Extraction Mechanism: Equipment used to continuously extract the solidified metal strand from the casting machine.
 Check Our Exclusive Product Offerings
Check Our Exclusive Product Offerings
Step-by-Step Process of Continuous Casting
- Melting: It all starts with raw materials melting down into a bubbling pool of molten metal.
- Transfer: Next, we transfer this molten marvel to the tundish, a sort of holding area before it’s ready for the main event.
- Casting: Now comes the exciting part. The molten metal flows from the tundish into the mould, where it starts to take shape.
- Solidification: As the metal cools inside the mould, it starts to solidify into the continuous strand we’re after.
- Extraction: Finally, the solidified metal strand is continuously extracted from the casting machine, ready to be used in various applications.
Understanding the inner workings of continuous casting machines is key to optimizing the efficiency and quality of metal production. Continuous casting machines are essential for optimizing process efficiency and product quality in metal production.
Types of Continuous Casting Machines
Continuous casting machines come in various configurations, each tailored to specific production needs and types of metal. Let’s take a look at the main types:
Vertical Continuous Casting Machines
Vertical continuous casting machines stand tall with their moulds positioned vertically above the tundish. Picture molten metal flowing downwards through the mould cavity, guided by gravity. These machines are perfect for producing cylindrical shapes like rods, tubes, and pipes.
Horizontal Continuous Casting Machines
Horizontal continuous casting machines, on the other hand, lay low with their moulds parallel to the ground. Here, molten metal is introduced into the mould from a tundish located above or beside it. This setup offers versatility, allowing for the production of various shapes like slabs, billets, and strips.
Curved Continuous Casting Machines
Curved continuous casting machines are the flexible ones of the bunch, designed to produce contoured metal shapes like railway tracks and beams. With their curved mould configuration, these machines let molten metal flow along a predetermined path to achieve the desired shape. They’re perfect for specialized applications that demand unique shapes.
Advantages of Continuous Casting
Continuous casting isn’t just a trend; it’s a tried-and-true method with some impressive perks. Let’s break it down:
Improved Product Quality
Continuous casting ensures top-notch product quality by minimizing internal defects and maintaining consistent properties throughout the metal strand. With controlled solidification and precise cooling, we get products with smooth surfaces, uniform properties, and tight tolerances.
Reduced Production Costs
By skipping intermediate steps and minimizing material waste, continuous casting cuts down on production costs. There’s less labour, less energy, and less material needed to produce the same amount of metal. Plus, the continuous nature of the process means we can churn out more products in less time, further boosting efficiency.
Increased Efficiency
Continuous casting machines are efficiency machines. They operate at high speeds, produce large quantities of metal products, and can switch between different grades and sizes with ease. With minimal downtime and seamless transitions between production runs, continuous casting keeps the metal flowing smoothly, day in and day out.
Continuous casting’s advantages aren’t just theoretical; they’re the real deal. By embracing this technology, manufacturers can produce high-quality metal products more efficiently and cost-effectively than ever before.
Challenges and Solutions
Even though continuous casting is a game-changer, it’s not without its hurdles. Here are some common challenges and how we tackle them:
Surface Defects
Surface defects like cracks and roughness can rear their heads during continuous casting due to various factors. To combat these, we optimize mould design, fine-tune cooling techniques, and keep a close eye on casting parameters. By ensuring uniform solidification and minimizing stress, we can nip surface defects in the bud.
Internal Quality Issues
Internal quality issues, such as shrinkage cavities and segregation, can lurk beneath the surface of continuous cast products. To tackle these, we employ advanced process control systems and tools like electromagnetic stirring devices. By promoting mixing and homogenization, we ensure that the final product meets the highest quality standards.
Maintenance Considerations
Continuous casting machines require regular TLC to keep them running smoothly. From cleaning and lubrication to replacing worn-out components, maintenance is key. By implementing preventive maintenance routines and leveraging predictive maintenance technologies, we minimize downtime and keep the production line humming.
Applications of Continuous Casting
Continuous casting isn’t just a one-trick pony; it has a wide range of applications across various industries:
Steel Industry
In the steel industry, continuous casting is the go-to method for producing slabs, billets, and blooms—the building blocks of many steel products. From construction to automotive, continuous casting ensures a steady supply of high-quality steel for various applications.
Aluminium Industry
Continuous casting plays a crucial role in the aluminium industry, where it’s used to produce ingots, billets, and extrusion logs. These products find their way into everything from automotive components to aerospace parts, thanks to continuous casting’s ability to deliver precise shapes and consistent properties.
Copper and Other Metals
Continuous casting isn’t just for steel and aluminium; it’s also used in the production of copper, brass, bronze, and other non-ferrous metals. These metals serve a myriad of industries, from electrical and electronics to plumbing and marine engineering.
Specialized Applications
Beyond traditional metalworking industries, continuous casting finds applications in specialized fields like ceramic and composite materials production. By continuously pushing the boundaries of what’s possible, continuous casting continues to drive innovation and efficiency across diverse industries.
Continuous casting isn’t just a manufacturing method; it’s a cornerstone of modern industry. By harnessing its capabilities, we can produce high-quality metal products efficiently and sustainably, meeting the demands of today’s ever-evolving market.
Importance of Ladle Turret Union in CCM & Deublin’s Offering
One critical component in continuous casting machines (CCM) is the ladle turret union, a pivotal connection point where the ladle transfers molten metal to the casting machine. This union must withstand high temperatures and pressure while maintaining a reliable seal to prevent metal leakage and ensure smooth operation of the casting process. Deublin, a leading provider of rotary unions and rotating joints, offers specialized solutions for ladle turret unions in continuous casting applications.
Deublin’s ladle turret unions are engineered with precision and durability in mind, utilizing advanced sealing technologies and robust construction materials to withstand the harsh conditions of continuous casting environments. These unions provide a leak-free connection between the ladle and the casting machine, ensuring efficient and reliable transfer of molten metal without interruption.
Deublin’s offering includes a range of ladle turret union designs tailored to meet the specific requirements of different continuous casting setups. Whether for vertical or horizontal casting machines, Deublin provides customized solutions that optimize performance and minimize downtime. With a focus on innovation and customer satisfaction, Deublin continues to drive advancements in ladle turret union technology, empowering metal producers to enhance productivity and quality in their continuous casting operations.
Frequently Asked Questions
1. What is continuous casting, and how does it revolutionize metal production?
Continuous casting is a method in metallurgy where molten metal is poured into a continuous casting machine and solidifies into a continuous strand of desired shape and dimensions. It revolutionizes metal production by allowing for seamless, uninterrupted production of high-quality metal shapes, reducing waste, and enhancing efficiency.
2. What types of metal shapes can be produced using continuous casting?
Continuous casting can produce a variety of metal shapes, including slabs, billets, blooms, rods, tubes, pipes, strips, and specialized contoured shapes like railway tracks and beams.
3. What are the advantages of continuous casting over traditional casting methods?
Continuous casting offers several advantages over traditional casting methods, including improved product quality, reduced production costs, and increased efficiency. It minimizes internal defects, maintains consistent properties throughout the metal strand, and streamlines the production process, resulting in higher productivity and profitability.
4. What are some common challenges faced in continuous casting, and how are they addressed?
Common challenges in continuous casting include surface defects, internal quality issues, and maintenance considerations. These challenges are addressed through optimization of mold design, cooling techniques, and casting parameters, as well as the implementation of advanced process control systems and preventive maintenance routines.
5. What are the main types of continuous casting machines?
The main types of continuous casting machines include vertical continuous casting machines, horizontal continuous casting machines, and curved continuous casting machines. Each type is designed to accommodate specific production requirements and metal types, offering versatility and flexibility in metal shaping.
6. How does continuous casting work step-by-step?
Continuous casting begins with melting raw materials in a furnace, followed by the transfer of molten metal to a continuous casting machine. The molten metal flows into a mold, where it solidifies into a continuous strand. The solidified metal strand is then extracted from the casting machine for further processing or use in downstream applications.
7. What are some applications of continuous casting in different industries?
Continuous casting finds applications in various industries, including the steel industry, aluminum industry, copper industry, and other non-ferrous metal industries. It is used to produce metal products for construction, automotive, aerospace, electrical, electronics, plumbing, marine engineering, and specialized applications such as ceramic and composite materials production.
8. How has continuous casting evolved over time?
Continuous casting has evolved significantly since its inception in the late 19th century, with advancements in metallurgical technology driving improvements in process efficiency, product quality, and versatility. Today, continuous casting is a cornerstone of modern metal production, driving innovation and sustainability in the global manufacturing sector.
9. What are some key components of continuous casting machines?
Key components of continuous casting machines include the tundish, mold, rollers, cooling system, and extraction mechanism. Each component plays a crucial role in shaping and solidifying the molten metal into the desired product.
10. How does continuous casting contribute to sustainability in metal production?
Continuous casting contributes to sustainability in metal production by minimizing material waste, reducing energy consumption, and optimizing resource utilization. By streamlining the production process and enhancing efficiency, continuous casting helps reduce the environmental footprint of metal manufacturing operations.
Conclusion
Continuous casting has revolutionized the metalworking industry, enabling the efficient and cost-effective production of high-quality metal products. From steel and aluminium to copper and alloys, continuous casting machines play a crucial role in shaping raw materials into a diverse range of shapes and sizes used in various applications. By eliminating intermediate processing steps and minimizing material waste, continuous casting enhances process efficiency, reduces production costs, and ensures product consistency and quality.
Despite its many advantages, continuous casting also presents challenges that metal producers must address through innovative solutions and technologies. Surface defects, internal quality issues, and maintenance considerations require careful attention to ensure optimal process performance and product quality. By implementing preventive maintenance routines, advanced process control systems, and digitalization strategies, manufacturers can enhance the reliability, efficiency, and sustainability of their continuous casting operations.
Looking ahead, continuous casting is poised to undergo further advancements driven by automation, advanced process control, and digitalization. By embracing these trends and developments, manufacturers can stay competitive in a rapidly evolving global marketplace while meeting the demands for high-quality metal products in an efficient and sustainable manner.